Introduction
BackupRepo is the storage repository for backup data. Currently, KubeBlocks supports configuring various object storage services as backup repositories, including OSS (Alibaba Cloud Object Storage Service), S3 (Amazon Simple Storage Service), COS (Tencent Cloud Object Storage), GCS (Google Cloud Storage), OBS (Huawei Cloud Object Storage), MinIO, and other S3-compatible services.
You can create multiple BackupRepos to suit different scenarios. For example, based on different businesses, the data of business A is stored in repository A, and the data of business B is stored in repository B. Or you can configure multiple repositories by region to realize geo-disaster recovery. But it is required to specify backup repositories when you create a backup. You can also create a default backup repository and KubeBlocks uses this default repository to store backup data if no specific repository is specified.
Before you start
Make sure you have all the following prepared.
- Install kbcli
- Install kubectl
- Install Helm
- Install KubeBlocks by kbcli or by Helm
Install MinIO
If you don't have an object storage service from a cloud provider, you can deploy the open-source service MinIO in Kubernetes and use it to configure BackupRepo. If you are using an object storage service provided by a cloud provider, directly skip to Configure BackupRepo.
Steps
-
Install MinIO in the
kb-systemnamespace.helm install minio oci://registry-1.docker.io/bitnamicharts/minio --namespace kb-system --create-namespace --set "extraEnvVars[0].name=MINIO_BROWSER_LOGIN_ANIMATION" --set "extraEnvVars[0].value=off"Get the initial username and password:
# Initial username
echo $(kubectl get secret --namespace kb-system minio -o jsonpath="{.data.root-user}" | base64 -d)
# Initial password
echo $(kubectl get secret --namespace kb-system minio -o jsonpath="{.data.root-password}" | base64 -d) -
Generate credentials.
Access the login page by running
kubectl port-forward --namespace kb-system svc/minio 9001:9001and then accessing127.0.0.1:9001.Once you are logged in to the dashboard, you can generate an
access keyandsecret key.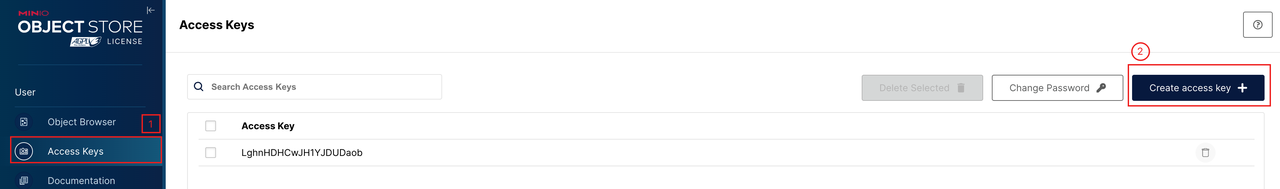
-
Create a bucket.
Create a bucket named
test-miniofor the test.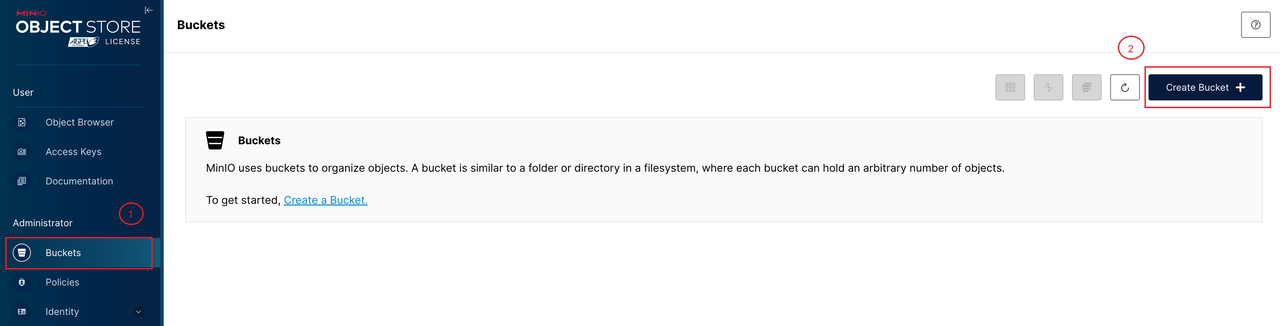
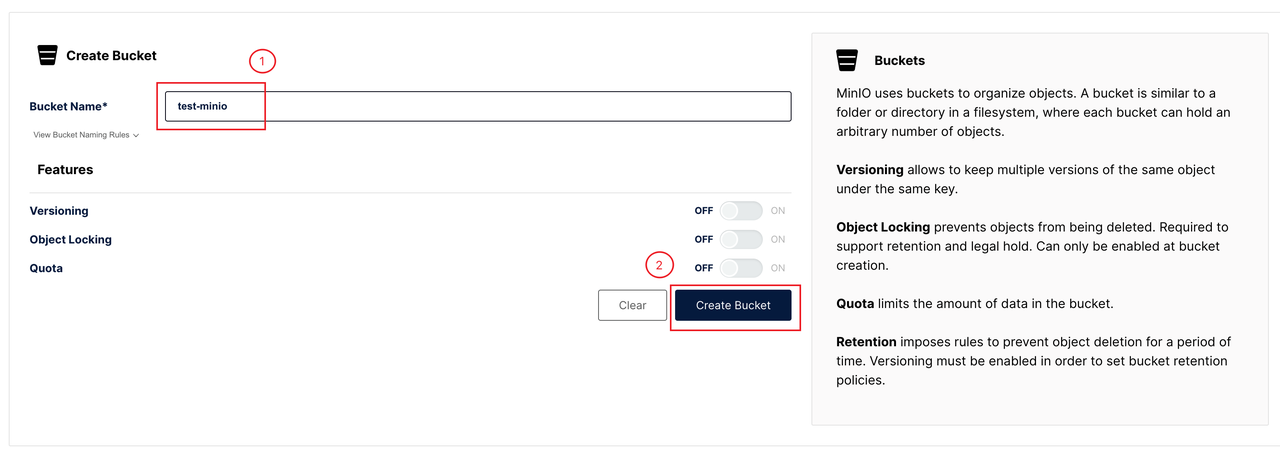
The access address (endpoint) for the installed MinIO is http://minio.kb-system.svc.cluster.local:9000, which will be used to configure BackupRepo. In this case, kb-system is the name of the namespace where MinIO is installed.
Configure BackupRepo
With object storage services prepared, it's time to configure BackupRepo. KubeBlocks provides two ways for the configuration:
- Automatic BackupRepo configuration during KubeBlocks installation;
- Manual BackupRepo configuration for on-demand scenarios.
Access BackupRepo
There are two methods to access remote object storage:
- Use command-line tools to directly access remote storage.
- Mount the remote storage to the local system with a CSI driver, allowing the work processes to access the remote storage as if it were local files.
The two access methods are referred to as "Tool" and "Mount". When creating BackupRepo, you can specify the access method through the accessMethod field, which can not be changed after creation.
Generally, it is recommended to use the "Tool" method as it does not require installing an additional CSI driver, thus reducing dependencies.
However, as backup and restore tasks require running in the namespace of the database cluster, using the "Tool" approach automatically synchronizes the necessary credentials for accessing the remote storage as secret resources in those namespaces. These credentials are used by the data transfer tool. If you have concerns about security risks associated with synchronizing secrets in a multi-tenant environment, you can choose to use the "Mount" method.
Manual BackupRepo configuration
If you do not configure the BackupRepo information when installing KubeBlocks, you can manually configure it by the following instructions.
-
Install the S3 CSI driver (only used in the Mount method).
- kbcli
- Helm
# Enable the CSI-S3 add-on
kbcli addon enable csi-s3
# You can add flags to customize the installation of this add-on
# CSI-S3 installs a daemonSet Pod on all nodes by default and you can set tolerations to install it on the specified node
kbcli addon enable csi-s3 \
--tolerations '[{"key":"taintkey","operator":"Equal","effect":"NoSchedule","value":"true"}]' \
--tolerations 'daemonset:[{"key":"taintkey","operator":"Equal","effect":"NoSchedule","value":"true"}]'
# View the status of CSI-S3 driver and make sure it is Enabled
kbcli addon list csi-s3helm repo add kubeblocks https://jihulab.com/api/v4/projects/85949/packages/helm/stable
helm install csi-s3 kubeblocks/csi-s3 --version=0.7.0 -n kb-system
# You can add flags to customize the installation of this add-on
# CSI-S3 installs a daemonSet Pod on all nodes by default and you can set tolerations to install it on the specified node
--set-json tolerations='[{"key":"taintkey","operator":"Equal","effect":"NoSchedule","value":"taintValue"}]'
--set-json daemonsetTolerations='[{"key":"taintkey","operator":"Equal","effect":"NoSchedule","value":"taintValue"}]' -
Create BackupRepo.
- kbcli
- kubectl
- S3
- OSS
- OBS
- COS
- GCS
- MinIO
kbcli backuprepo create my-repo \
--provider s3 \
--region cn-northwest-1 \
--bucket test-kb-backup \
--access-key-id <ACCESS KEY> \
--secret-access-key <SECRET KEY> \
--access-method Tool \
--defaultYou can also specify
--access-methodasMount.kbcli backuprepo create my-repo \
--provider oss \
--region cn-zhangjiakou \
--bucket test-kb-backup \
--access-key-id <ACCESS KEY> \
--secret-access-key <SECRET KEY> \
--access-method Tool \
--defaultYou can also explicitly specify the OSS endpoint using the
--endpointflag. For example,kbcli backuprepo create my-repo \
--provider oss \
--region cn-zhangjiakou \
--bucket test-kb-backup \
--endpoint https://oss-cn-zhangjiakou-internal.aliyuncs.com \
--access-key-id <ACCESS KEY> \
--secret-access-key <SECRET KEY> \
--access-method Tool \
--defaultkbcli backuprepo create my-repo \
--provider obs \
--region cn-north-4 \
--bucket test-kb-backup \
--access-key-id <ACCESS KEY> \
--secret-access-key <SECRET KEY> \
--access-method Tool \
--defaultFor COS, the naming format of a bucket is
<BucketName-APPID>,where APPID is automatically generated by Tencent Cloud. When setting--bucket, first create the bucket on the Tencent Cloud console and retrieve the bucket name.kbcli backuprepo create my-repo \
--provider cos \
--region ap-guangzhou \
--bucket test-kb-backup \
--access-key-id <ACCESS KEY> \
--secret-access-key <SECRET KEY> \
--access-method Tool \
--defaultkbcli backuprepo create my-repo \
--provider gcs-s3comp \
--region auto \
--bucket test-kb-backup \
--access-key-id <ACCESS KEY> \
--secret-access-key <SECRET KEY> \
--access-method Tool \
--defaultGCS supported by KubeBlocks is the S3-compatible version provided by Google Cloud.
kbcli backuprepo create my-repo \
--provider minio \
--endpoint <ip:port> \
--bucket test-minio \
--access-key-id <ACCESS KEY> \
--secret-access-key <SECRET KEY> \
--access-method Tool \
--defaultThe address for the deployed MinIO is http://minio.kb-system.svc.cluster.local:9000.
The above command creates a default backup repository
my-repo.my-repois the name of the created backup repository. If you do not specify a name, the system creates a random name, following the formatbackuprepo-xxxxx.--defaultmeans that this repository is set as the default repository. Note that there can only be one default global repository. If there exist multiple default repositories, KubeBlocks cannot decide which one to use (similar to the default StorageClass of Kubernetes), which further results in backup failure. Using kbcli to create BackupRepo can avoid such problems because kbcli checks whether there is another default repository before creating a new one.--providerspecifies the storage type, i.e.storageProvider, and is required for creating a BakcupRepo. The available values ares3,cos,gcs-s3comp,obs,oss,minio,ftp, andnas. Parameters for different storage providers vary and you can runkbcli backuprepo create --provider STORAGE-PROVIDER-NAME -hto view the flags for different storage providers. Please note that--provideris mandatory in configuration.
After
kbcli backuprepo createis executed successfully, the system creates the K8s resource whose type isBackupRepo. You can modify the annotation of this resource to adjust the default repository.# Cancel the default repository
kubectl annotate backuprepo old-default-repo \
--overwrite=true \
dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/is-default-repo=false# Set a new default repository
kubectl annotate backuprepo backuprepo-4qms6 \
--overwrite=true \
dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/is-default-repo=truekubectlis another option to create BackupRepo, but the commands do not include parameter and default repository verification compared with kbcli, which is not convenient. It is recommended to use kbcli.- S3
- OSS
- OBS
- COS
- GCS
- MinIO
# Create a secret to save the access key for S3
kubectl create secret generic s3-credential-for-backuprepo \
-n kb-system \
--from-literal=accessKeyId=<ACCESS KEY> \
--from-literal=secretAccessKey=<SECRET KEY>
# Create the BackupRepo resource
kubectl apply -f - <<-'EOF'
apiVersion: dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/v1alpha1
kind: BackupRepo
metadata:
name: my-repo
annotations:
dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/is-default-repo: "true"
spec:
storageProviderRef: s3
accessMethod: Tool
pvReclaimPolicy: Retain
volumeCapacity: 100Gi
config:
bucket: test-kb-backup
endpoint: ""
mountOptions: --memory-limit 1000 --dir-mode 0777 --file-mode 0666
region: cn-northwest-1
credential:
name: s3-credential-for-backuprepo
namespace: kb-system
EOF# Create a secret to save the access key for OSS
kubectl create secret generic oss-credential-for-backuprepo \
-n kb-system \
--from-literal=accessKeyId=<ACCESS KEY> \
--from-literal=secretAccessKey=<SECRET KEY>
# Create the BackupRepo resource
kubectl apply -f - <<-'EOF'
apiVersion: dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/v1alpha1
kind: BackupRepo
metadata:
name: my-repo
annotations:
dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/is-default-repo: "true"
spec:
storageProviderRef: oss
accessMethod: Tool
pvReclaimPolicy: Retain
volumeCapacity: 100Gi
config:
bucket: test-kb-backup
mountOptions: ""
endpoint: ""
region: cn-zhangjiakou
credential:
name: oss-credential-for-backuprepo
namespace: kb-system
EOF# Create a secret to save the access key for OBS
kubectl create secret generic obs-credential-for-backuprepo \
-n kb-system \
--from-literal=accessKeyId=<ACCESS KEY> \
--from-literal=secretAccessKey=<SECRET KEY>
# Create the BackupRepo resource
kubectl apply -f - <<-'EOF'
apiVersion: dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/v1alpha1
kind: BackupRepo
metadata:
name: my-repo
annotations:
dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/is-default-repo: "true"
spec:
storageProviderRef: obs
accessMethod: Tool
pvReclaimPolicy: Retain
volumeCapacity: 100Gi
config:
bucket: test-kb-backup
mountOptions: ""
endpoint: ""
region: cn-north-4
credential:
name: obs-credential-for-backuprepo
namespace: kb-system
EOF# Create a secret to save the access key for COS
kubectl create secret generic cos-credential-for-backuprepo \
-n kb-system \
--from-literal=accessKeyId=<ACCESS KEY> \
--from-literal=secretAccessKey=<SECRET KEY>
# Create the BackupRepo resource
kubectl apply -f - <<-'EOF'
apiVersion: dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/v1alpha1
kind: BackupRepo
metadata:
name: my-repo
annotations:
dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/is-default-repo: "true"
spec:
storageProviderRef: cos
accessMethod: Tool
pvReclaimPolicy: Retain
volumeCapacity: 100Gi
config:
bucket: test-kb-backup
mountOptions: ""
endpoint: ""
region: ap-guangzhou
credential:
name: cos-credential-for-backuprepo
namespace: kb-system
EOF# Create a secret to save the access key for GCS
kubectl create secret generic gcs-credential-for-backuprepo \
-n kb-system \
--from-literal=accessKeyId=<ACCESS KEY> \
--from-literal=secretAccessKey=<SECRET KEY>
# Create the BackupRepo resource
kubectl apply -f - <<-'EOF'
apiVersion: dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/v1alpha1
kind: BackupRepo
metadata:
name: my-repo
annotations:
dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/is-default-repo: "true"
spec:
storageProviderRef: gcs
accessMethod: Tool
pvReclaimPolicy: Retain
volumeCapacity: 100Gi
config:
bucket: test-kb-backup
mountOptions: ""
endpoint: ""
region: auto
credential:
name: gcs-credential-for-backuprepo
namespace: kb-system
EOF# Create a secret to save the access key for MinIO
kubectl create secret generic minio-credential-for-backuprepo \
-n kb-system \
--from-literal=accessKeyId=<ACCESS KEY> \
--from-literal=secretAccessKey=<SECRET KEY>
# Create the BackupRepo resource
kubectl apply -f - <<-'EOF'
apiVersion: dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/v1alpha1
kind: BackupRepo
metadata:
name: my-repo
annotations:
dataprotection.kubeblocks.io/is-default-repo: "true"
spec:
storageProviderRef: minio
accessMethod: Tool
pvReclaimPolicy: Retain
volumeCapacity: 100Gi
config:
bucket: test-kb-backup
mountOptions: ""
endpoint: <ip:port>
credential:
name: minio-credential-for-backuprepo
namespace: kb-system
EOF -
View the BackupRepo and its status. If the status is
Ready, the BackupRepo is ready.- kbcli
- kubectl
kbcli backuprepo listkubectl get backuprepo
If the BackupRepo status shows Failed or remains in PreChecking for a long time, run kubectl describe backuprepo my-repo or kbcli backuprepo describe my-repo to check the status.conditions for details.
To troubleshoot:
- Check whether configuration parameters, such as
endpoint,accessKeyId, andsecretAccessKey, are correctly specified. - For self-hosted object storage (e.g., Ceph Object Storage), try using
minioas StorageProvider. The defaults3StorageProvider uses a virtual hosting URL style, which some self-hosted storage may not support. - If an
InvalidLocationConstrainterror occurs, check whether its parameter is correctly configured. If this error persists, leave theregionparameter empty and try again. - If the status remains in the
PreCheckingstate, check your network connection. Ensure the storage service is accessible from within the Kubernetes cluster. You can test this by running a Pod and connecting to the storage service using the corresponding client. - KubeBlocks uses rclone internally for data transfer. Check whether rclone can successfully access the storage service.
Automatic BackupRepo configuration
You can specify the BackupRepo information in a YAML configuration file when installing KubeBlocks, and KubeBlocks will create the BackupRepo and automatically install the necessary CSI Driver based on the provided configuration.
-
Prepare the configuration file.
Taking AWS S3 as an example, the configuration file
backuprepo.yamlis:backupRepo:
create: true
storageProvider: s3
config:
region: cn-northwest-1
bucket: test-kb-backup
secrets:
accessKeyId: <ACCESS KEY>
secretAccessKey: <SECRET KEY>region: specifies the region where S3 is located.bucket: specifies the bucket name of S3.accessKeyId: specifies the Access Key of AWS.secretAccessKey: specifies the Secret Key of AWS.storageProvider:specifies the object storage provider, which is S3 in this case.
- In KubeBlocks, the available
storageProvideroptions ares3,cos,gcs-s3comp,obs,oss,minio,ftp, andnfs. - For different
storageProvider, the configuration may differ.configandsecretsin the above example are applied to S3. - Execute the command
kubectl get storageproviders.storage.kubeblocks.ioto view the supportedstorageProvideroptions.
-
Specify the configuration file when installing KubeBlocks.
kbcli kubeblocks install -f backuprepo.yamlUse the command below to check the BackupRepo after installation.
- kbcli
- kubectl
kbcli backuprepo listkubectl get backuprepo