Connect database in production environment
In the production environment, it is normal to connect a database with CLI and SDK clients. There are three scenarios.
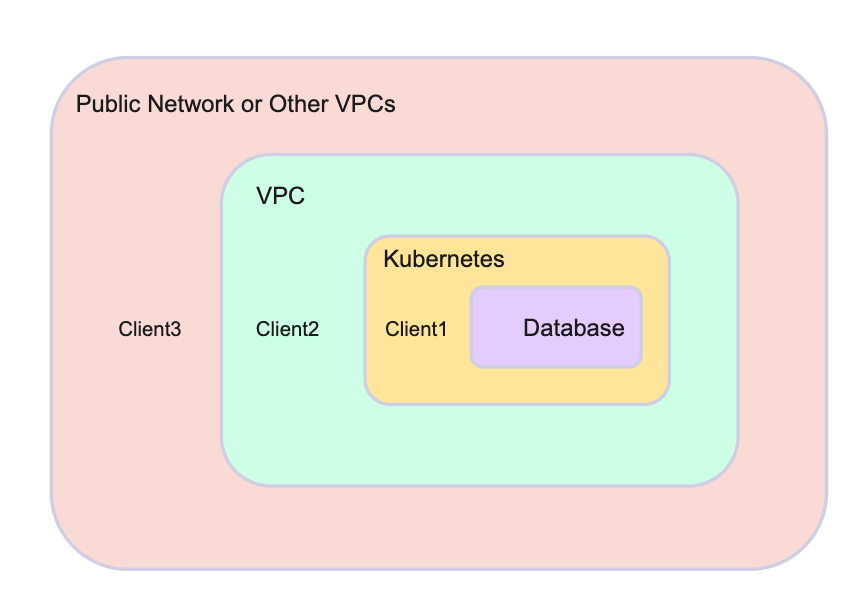
- Scenario 1: Client1 and the database are in the same Kubernetes cluster. To connect client1 and the database, see Use ClusterIP.
- Scenario 2: Client2 is outside the Kubernetes cluster, but it is in the same VPC as the database. To connect client2 and the database, see Expose VPC Private Address.
- Scenario 3: Client3 and the database are in different VPCs, such as other VPCs or the public network. To connect client3 and the database, see Expose VPC Public Address.
See the figure below to get a clear image of the network location.
Scenario 1. Connect database in the same Kubernetes cluster
You can connect with the database ClusterIP or domain name.
To check the database endpoint, use kubectl get service <cluster-name>-<component-name>.
kubectl get service mycluster-mysql
To check the database endpoint, use kbcli cluster describe ${cluster-name}.
kbcli cluster describe x
>
Name: x Created Time: Mar 01,2023 11:45 UTC+0800
NAMESPACE CLUSTER-DEFINITION VERSION STATUS TERMINATION-POLICY
default apecloud-mysql ac-mysql-8.0.30 Running Delete
Endpoints:
COMPONENT MODE INTERNAL EXTERNAL
x ReadWrite x-mysql.default.svc.cluster.local:3306 <none>
Topology:
COMPONENT INSTANCE ROLE STATUS AZ NODE CREATED-TIME
mysql x-mysql-0 leader Running cn-northwest-1b ip-10-0-2-184.cn-northwest-1.compute.internal/10.0.2.184 Mar 01,2023 11:45 UTC+0800
Resources Allocation:
COMPONENT DEDICATED CPU(REQUEST/LIMIT) MEMORY(REQUEST/LIMIT) STORAGE-SIZE STORAGE-CLASS
mysql false 1 / 1 1Gi / 1Gi data:10Gi <none>
Images:
COMPONENT TYPE IMAGE
mysql mysql registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/apecloud/apecloud-mysql-server:8.0.30-5.alpha2.20230105.gd6b8719.2
Events(last 5 warnings, see more:kbcli cluster list-events -n default x):
TIME TYPE REASON OBJECT MESSAGE
Scenario 2. Client outside the Kubernetes cluster but in the same VPC as the Kubernetes cluster
A stable domain name for long-term connections is required. An Internal LoadBalancer provided by the cloud vendor can be used for this purpose.
The following command creates a LoadBalancer instance for the database instance, which may incur expenses from your cloud vendor.
This example uses a MySQL cluster to demonstrate how to expose a VPC address on Alibaba Cloud.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apps.kubeblocks.io/v1alpha1
kind: OpsRequest
metadata:
name: ops-expose-enable
namespace: demo
spec:
clusterName: mycluster
expose:
- componentName: mysql
services:
- name: vpc
roleSelector: leader
serviceType: LoadBalancer
switch: Enable
preConditionDeadlineSeconds: 0
type: Expose
kbcli cluster expose ${cluster-name} --type vpc --enable=true
To disable the LoadBalancer instance, execute the following command.
Once disabled, the instance is not accessible.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apps.kubeblocks.io/v1alpha1
kind: OpsRequest
metadata:
name: ops-expose-disable
namespace: demo
spec:
clusterName: mycluster
expose:
- componentName: mysql
services:
- name: vpc
roleSelector: leader
serviceType: LoadBalancer
switch: Disable
preConditionDeadlineSeconds: 0
type: Expose
kbcli cluster expose ${cluster-name} --type vpc --enable=false
Scenario 3. Connect database with clients in other VPCs or public networks
If the client is in a different VPC and requires public access, you can enable the cloud vendor's External LoadBalancer.
The following command creates a LoadBalancer instance for the database instance, which may incur expenses from your cloud vendor.
The example uses MySQL to demonstrate how to expose the public address on Alibaba Cloud.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apps.kubeblocks.io/v1alpha1
kind: OpsRequest
metadata:
name: ops-expose-enable
namespace: demo
spec:
clusterName: mycluster
expose:
- componentName: mysql
services:
- name: internet
roleSelector: leader
serviceType: LoadBalancer
switch: Enable
preConditionDeadlineSeconds: 0
type: Expose
kbcli cluster expose ${cluster-name} --type internet --enable=true
To disable the LoadBalancer instance, execute the following command.
kubectl apply -f - <<EOF
apiVersion: apps.kubeblocks.io/v1alpha1
kind: OpsRequest
metadata:
name: ops-expose-disable
namespace: demo
spec:
clusterName: mycluster
expose:
- componentName: mysql
services:
- name: internet
roleSelector: leader
serviceType: LoadBalancer
switch: Disable
preConditionDeadlineSeconds: 0
type: Expose
kbcli cluster expose ${cluster-name} --type internet --enable=false
The instance is inaccessible after you disable the LoadBalancer instance.