Try out KubeBlocks in 5 minutes on laptop
This guide walks you through the quickest way to get started with KubeBlocks, demonstrating how to create a demo environment (Playground) with one command.
Before you start
Meet the following requirements for a smooth user experience:
-
Minimum system requirements:
- CPU: 4 cores, use
sysctl hw.physicalcpucommand to check CPU; - RAM: 4 GB, use
top -dcommand to check memory.
- CPU: 4 cores, use
-
Make sure the following tools are installed on your laptop:
Initialize Playground
Steps:
-
Install Playground.
kbcli playground initThis command:
- Creates a Kubernetes cluster in the container with K3d.
- Deploys KubeBlocks in the K3d cluster.
- Creates a standalone MySQL cluster.
note-
If you previously ran
kbcli playground initand it failed, running it again may cause errors. Please run thekbcli playground destroycommand first to clean up the environment, then runkbcli playground initagain. -
If you run Playground on Windows and the error below occurs, it is caused by the safety strategy of Windows 11 and the
kbcli.exeyou operate might be tampered with by a third party (or when you built the kbcli binary file through source on Windows).
error: failed to set up k3d cluster: failed to create k3d cluster kb-playground: Failed Cluster Start: Failed to start server k3d-kb-playground-server-0: Node k3d-kb-playground-server-0 failed to get ready: error waiting for log line `k3s is up and running` from node 'k3d-kb-playground-server-0': stopped returning log linesYou can follow the steps to solve this problem.
- Uninstall or delete the current
kbcli.exe. - Download the latest kbcli by
wingetor visit the GitHub release page of KubeBlocks to download kbcli again.
-
Check the MySQL cluster repeatedly until the status becomes
Running.kbcli cluster listResult:
You just created a cluster named
myclusterin the default namespace. You can find the user guide under the installation success tip. View this guide again by runningkbcli playground init -h.
Try KubeBlocks with Playground
You can explore KubeBlocks, by referring to Describe a MySQL cluster, Access a MySQL cluster, Observe a MySQL cluster, and High availability. Go through the following instructions to try basic features of KubeBlocks.
Describe a MySQL cluster
Steps:
-
View the database cluster list.
kbcli cluster list -
View the details of a specified database cluster, such as
STATUS,Endpoints,Topology,Images, andEvents.kbcli cluster describe mycluster
Access a MySQL cluster
Option 1. Connect database from container network.
Wait until the status of this cluster is Running, then run kbcli cluster connect to access a specified database cluster. For example,
kbcli cluster connect mycluster
Option 2. Connect database from host network.
Steps:
-
Get Credentials.
kbcli cluster connect --show-example --client=cli mycluster -
Run
port-forward.kubectl port-forward service/mycluster-mysql 3306:3306
>
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:3306 -> 3306
Forwarding from [::1]:3306 -> 3306 -
Open another terminal tab to connect the database cluster.
mysql -h 127.0.0.1 -P 3306 -u root -paiImelyt
>
...
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql> show databases;
>
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| mydb |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
+--------------------+
5 rows in set (0.02 sec)
Observe a MySQL cluster
KubeBlocks supports complete observability capabilities. This section demonstrates the monitoring function of KubeBlocks.
Steps:
-
Open the grafana dashboard.
kbcli dashboard open kubeblocks-grafanaResult:
A monitoring page on Grafana website is loaded automatically after the command is executed.
-
Click the Dashboard icon on the left bar and monitoring panels show on the page.
-
Click General -> MySQL to monitor the status of the MySQL cluster.
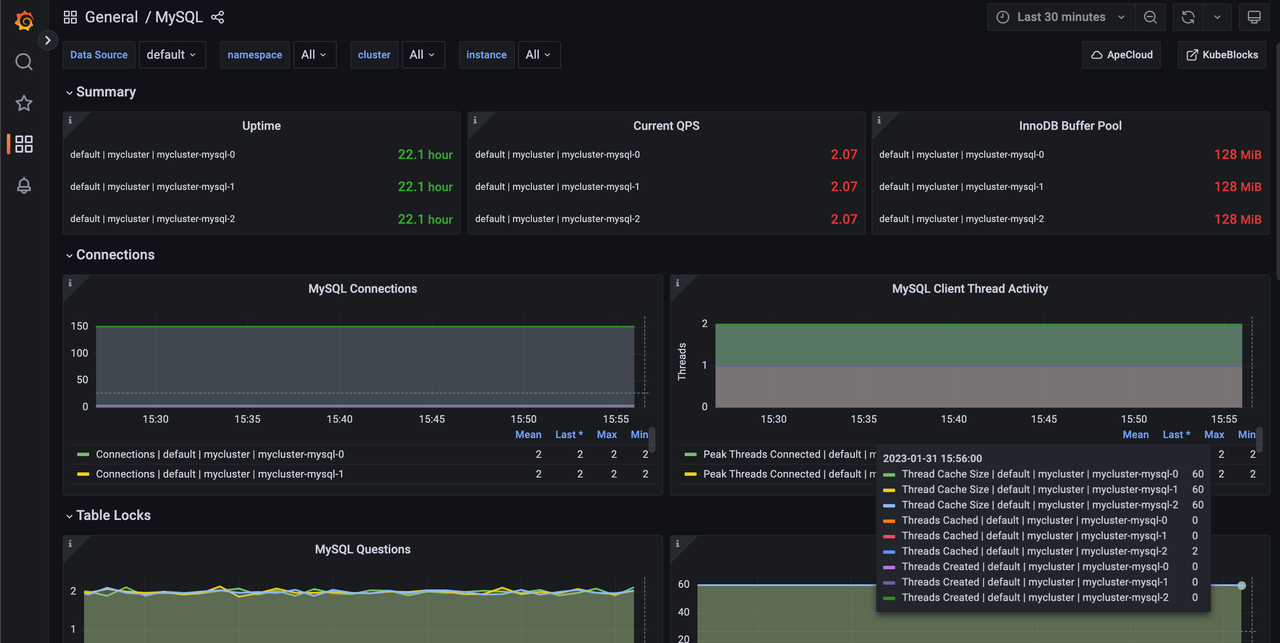
High availability of MySQL
This guide shows a simple failure simulation to show you the failure recovery capability of MySQL.
Delete the Standalone MySQL cluster
Delete the Standalone MySQL cluster before trying out high availability.
kbcli cluster delete mycluster
Create a Raft MySQL cluster
You can use kbcli to create a Raft MySQL cluster. The following is an example of creating a Raft MySQL cluster with default configurations.
kbcli cluster create --cluster-definition='apecloud-mysql' --set replicas=3
Simulate leader pod failure recovery
In this example, delete the leader pod to simulate a failure.
Steps:
-
Make sure the newly created cluster is
Running.kbcli cluster list -
Find the leader pod name in
Topology. In this example, the leader pod's name is maple05-mysql-1.kbcli cluster describe maple05
>
Name: maple05 Created Time: Jan 27,2023 17:33 UTC+0800
NAMESPACE CLUSTER-DEFINITION VERSION STATUS TERMINATION-POLICY
default apecloud-mysql ac-mysql-8.0.30 Running WipeOut
Endpoints:
COMPONENT MODE INTERNAL EXTERNAL
mysql ReadWrite 10.43.29.51:3306 <none>
Topology:
COMPONENT INSTANCE ROLE STATUS AZ NODE CREATED-TIME
mysql maple05-mysql-1 leader Running <none> k3d-kubeblocks-playground-server-0/172.20.0.3 Jan 30,2023 17:33 UTC+0800
mysql maple05-mysql-2 follower Running <none> k3d-kubeblocks-playground-server-0/172.20.0.3 Jan 30,2023 17:33 UTC+0800
mysql maple05-mysql-0 follower Running <none> k3d-kubeblocks-playground-server-0/172.20.0.3 Jan 30,2023 17:33 UTC+0800
Resources Allocation:
COMPONENT DEDICATED CPU(REQUEST/LIMIT) MEMORY(REQUEST/LIMIT) STORAGE-SIZE STORAGE-CLASS
mysql false <none> <none> <none> <none>
Images:
COMPONENT TYPE IMAGE
mysql mysql docker.io/apecloud/wesql-server:8.0.30-5.alpha2.20230105.gd6b8719
Events(last 5 warnings, see more:kbcli cluster list-events -n default mycluster):
TIME TYPE REASON OBJECT MESSAGE -
Delete the leader pod.
kubectl delete pod maple05-mysql-1
>
pod "maple05-mysql-1" deleted -
Connect to the Raft MySQL cluster. It can be accessed within seconds.
kbcli cluster connect maple05
>
Connect to instance maple05-mysql-2: out of maple05-mysql-2(leader), maple05-mysql-1(follower), maple05-mysql-0(follower)
Welcome to the MySQL monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 33
Server version: 8.0.30 WeSQL Server - GPL, Release 5, Revision d6b8719
Copyright (c) 2000, 2022, Oracle and/or its affiliates.
Oracle is a registered trademark of Oracle Corporation and/or its
affiliates. Other names may be trademarks of their respective
owners.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
mysql>
Demonstrate availability failure by NON-STOP NYAN CAT (for fun)
The above example uses kbcli cluster connect to test availability, in which the changes are not obvious to see.
NON-STOP NYAN CAT is a demo application to observe how the database cluster exceptions affect actual businesses. Animations and real-time key information display provided by NON-STOP NYAN CAT can directly show the availability influences of database services.
Steps:
-
Install the NYAN CAT demo application.
kbcli addon enable nyancatExpected output
addon.extensions.kubeblocks.io/nyancat enabled -
Check the NYAN CAT add-on status and when its status is
Enabled, this application is ready.kbcli addon list | grep nyancat -
Open the web page.
kbcli dashboard open kubeblocks-nyancat -
Open another terminal tab and delete the leader pod. Then view the influences on the Raft MySQL cluster through the NYAN CAT page.
kubectl delete pod maple05-mysql-1
-
Uninstall the NYAN CAT demo application after your trial.
kbcli addon disable nyancat
Destroy Playground
Destroying Playground cleans up resources and data:
- Delete all KubeBlocks database clusters.
- Uninstall KubeBlocks.
- Delete the Kubernetes cluster created by K3d.
Destroy Playground.
kbcli playground destroy