Migrate data in PostgreSQL by KubeBlocks
Environment and aim
-
Source: PostgreSQL version 14 installed by Pigsty on Alibaba Cloud ECS. PostGIS plugin is also installed and the open-source map data is imported by osm2pgsql.
-
Sink: PostgreSQL version 14.7.0 installed by KubeBlocks on AWS EKS. No plugin is installed.
-
Aim: Migrate db_test.public.table_test_1 and db_test.public.table_test2 in the source to the sink.
Before you start
Enable kbcli migration
-
Install KubeBlocks: You can install KubeBlocks by kbcli or by Helm.
-
kbcli addon list
kbcli addon enable migration
Configure the source
Modify the configuration of the source to support CDC.
- Set 'wal_level' configuration to 'logical'.
- Make sure that the number of 'max_replication_slots' configured is sufficient.
- Make sure that the number of 'max_wal_senders' configured is sufficient.
- If you install PostgreSQL by Pigsty, you can modify the configuration by executing the
pg edit-configcommand. - Modifying WAL (Write Ahead Log) configuration restarts the database. Make sure the modification is performed during off-peak hours.
Check the account permission
Make sure both the source and sink account meet the following permissions.
- The source account
- LOGIN permission
- The read permission of the source migration objects
- REPLICATION permission
- The sink account
- LOGIN permission
- The read/write permission of the sink
Initialize the sink
-
Create a database named
db_test.create database db_test; -
Install PostGIS and import osm data.
- Install PostGIS. If you install PostgreSQL by Pigsty, PostGIS is built-in and you can execute
CREATE EXTENSIONaccording to your need. - Import osm data.
- Install PostGIS. If you install PostgreSQL by Pigsty, PostGIS is built-in and you can execute
For the migration function in KubeBlocks version 5.0, there are limits for the structure initialization.
- User-defined types are not supported.
- A field filled with an Array data type (such as text[], text[3][3], and integer[]) is not supported for migration.
Prepare data sampling
It is recommended to prepare data sampling for verification after the migration to ensure correctness.
Migrate data
Steps
-
Create a migration task.
kbcli migration create mytask --template apecloud-pg2pg \
--source user:123456@127.0.0.1:5432/db_test \
--sink user:123456@127.0.0.2:5432/db_test \
--migration-object '"public.table_test_1","public.table_test_2"'📎 Table 1. Options explanation
Option Descriprion mystask The name of the migration task. You can customize it. --templateIt specifies the migration template. --template apecloud-pg2pgmeans that this migration task uses the template of migrating from PostgreSQL to PostgreSQL created by KubeBlocks. Runkbcli migration templatesto view all available templates and the supported database information.--sourceIt specifies the source. user:123456@127.0.0.1:5432/db_testin the above example follows the format${user_name}:${password}@${database connection url}/${database}. For this guide, the connection URL uses the public network address.--sinkIt specifies the destination. user:123456@127.0.0.2:5432/db_testin the above example follows the format${user_name}:${password}@${database connection url}/${database}. For this guide, the connection URL uses the service address inside the Kubernetes cluster.--migration-objectIt specifies the migration object. The above example describes data in "public.table_test_1" and "public.table_test_2", including structure data, stock data, and incremental data generated during running migration task, will be migrated to the sink. noteAn example of the
--sinkURL: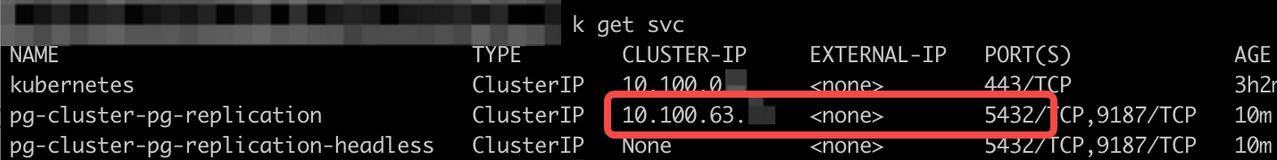
-
(Optional) Specify migration steps by the flag
--steps.The default steps follow the order precheck -> structure initialization -> data initialization -> incremental migration. You can use
--stepsto specify migration steps. For example, perform tasks in the order of precheck, full initialization, and incremental migration.kbcli migration create mytask --template apecloud-pg2pg \
--source user:123456@127.0.0.1:5432/db_test \
--sink user:123456@127.0.0.2:5432/db_test \
--migration-object '"public.table_test_1","public.table_test_2"'
--steps precheck=true,init-struct=false,init-data=true,cdc=true -
View the task status.
# View the migration task list
kbcli migration list
# View the details of a specified task
kbcli migration describe ${migration-task-name}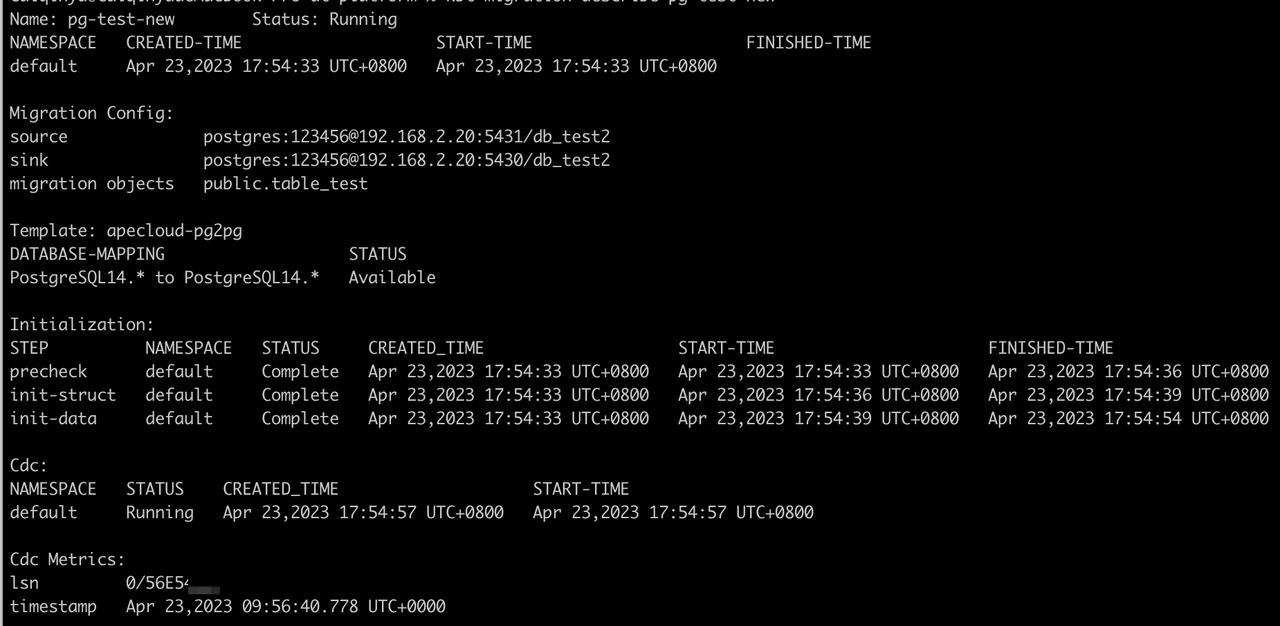
Pay attention to Initialization, CDC, and CDC Metrics.
-
Initialization
- Precheck: If the status shows
Failed, it means the initialization precheck does not pass. Troubleshoot the initialization by the following examples in troubleshooting. - Init-struct: Structure initialization. Idempotent processing logic is adopted. A failure occurs only when a severe problem occurs, such as failing to connect a database.
- Init-data: Data initialization. If there is a large amount of stock data, it takes a long time to perform this step and you should pay attention to Status.
- Precheck: If the status shows
-
CDC: Incremental migration. Based on the timestamp recorded by the system before the init-data step, the system starts data migration following eventual consistency and performs capturing the source library WAL (Write Ahead Log) changes -> writing to the sink. Under normal circumstances, the CDC phase continues if the migration link is not actively terminated.
-
CDC Metrics: Incremental migration indicators. Currently, the indicators mainly provide the WAL LSN (Log Sequencer Number) of the source library and the corresponding timestamp (note that the timestamp shows the local time zone of the Pod Container runtime) when the CDC process has completed "capturing -> writing" process.
noteThe CDC Metrics are updated every 10 minutes by the system, i.e. if there exists continuous data writing into the source, metrics.timestamp here delays 10 minutes compared with the current time.
-
-
Validate the migration with the prepared data sampling.
Troubleshooting
If any step above fails, run the command below to troubleshoot the failure.
# --step: Specify the step. Allowed values: precheck,init-struct,init-data,cdc
kbcli migration logs ${migration-task-name} --step ${step-name}
Switch applications
Before you start
-
Make sure the KubeBlocks migration task runs normally.
-
To differentiate the dialogue information and to improve data security, it is recommended to create and authorize another account dedicated to data migration.
-
For safety concerns, it is necessary to stop the business write and switch the application during off-peak hours.
-
Before switching the application, it is recommended to prepare data sampling for verification after switching to ensure correctness.
-
Pay attention to serial, sequence, and slot.
-
Serial and sequence
Search and record the max. value of Sequence before switching applications and set it as the initial value of Sequence in the sink.
After the business is switched to the sink, the new written Sequence does not take the max. value in the source as the initial value to continue in an increment order by default. You need to set it manually.
# PostgreSQL Function Sample:
CREATE FUNCTION build_setvals() returns void
AS $$
declare
nsp name;
rel name;
val int8;
begin
for nsp,rel in select nspname,relname from pg_class t2 , pg_namespace t3 where t2.relnamespace=t3.oid and t2.relkind='S'
loop
execute format($_$select last_value from %I.%I$_$, nsp, rel) into val;
raise notice '%',
format($_$select setval('%I.%I'::regclass, %s);$_$, nsp, rel, val+1);
end loop;
end;
$$
LANGUAGE plpgsql;
# Execute:
psql -hxx -p xx -U xx -d xx -c "set client_min_messages = notice; select build_setvals();" | grep setval
# Output like:
NOTICE: select setval('public.seq_test_1'::regclass, 2);
NOTICE: select setval('public.seq_test_2'::regclass, 1001);
NOTICE: select setval('public.seq_test_3'::regclass, 203);
NOTICE: select setval('public.seq_test_4'::regclass, 476);
# Execute the above script in the sink -
Slot lifecycle
The CDC phase (the incremental migration) relies on the slot. A replication slot and publication are created during the CDC phase and these metadata should be deleted first before deleting the migration task metadata.
If the incremental migration is performed, the migration task creates a replication slot named after the task name during the initialization phase of the init-data step (hyphens, "-", in the task name are replaced with underlines, "_"). When the incremental migration starts, the migration task creates a publication with the previous replication slot name and "_publication_for_all_tables" in the name to perform WAL consumption.
When the migration task is deleted (running
kbcli migration terminate), this task changes to the Terminating status. The termination operation first stops the CDC process, then tries to clear the above replication slot and publication. Only when the above metadata are cleared, is the metadata of the migration task deleted.noteIf the slot is not cleaned up, it affects the log-cleaning logic in PostgreSQL. When the PostgreSQL disk is insufficient and a redundant slot prevents the log from being cleaned up, a serious failure may occur.
Therefore, the migration task can be deleted only when the slot cleanup is completed. If there is a PostgreSQL task that keeps the Terminating status for a long time, you need to pay attention to the status of the slot and disk water level and intervene manually when necessary.
Cleanup operations adopt the idempotent logic, and the reasons for general cleanup failures include but are not limited to the following:
- While the migration task is running, the connection string of the source library changes, which causes the migration task cannot connect to the source.
- While the migration task is running, the account and password of the source change, which causes the migration task cannot connect to the source.
- While the migration task is running, the permissions of the source library account change, which causes the migration task cannot be deleted.
Steps
-
Check the migration task status and ensure the task is performed normally.
-
Describe the migration task details and all steps in Initialization are
Completeand CDC isRunning.kbcli migration describe ${migration-task-name} -
Under the prerequisite that there exists continuous write into the source, observe whether the timestamp is still in progress and whether there is almost no delay. For example,
kbcli migration logs ${migration-task-name} --step cdc | grep current_positionThe results update every 10 seconds.
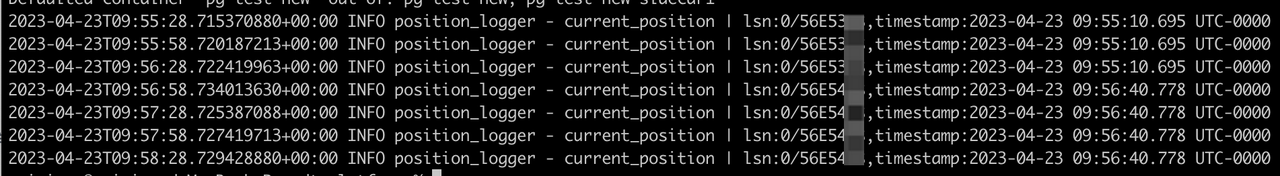
-
-
Pause the business and stop new business data from being written into the source.
-
View the migration status again and ensure the migration task runs normally, lasting at least one minute.
Refer to the operations in step 1 and observe whether the link is normal and the timestamp meets the expectation.
-
Use the sink to restore the business.
-
Validate the switch with the prepared data sampling.
Clean up the environment
After the migration task is completed, you can terminate the migration task and function.
Terminate the migration task
Deleting the migration task does not affect the data in the source and sink.
kbcli migration terminate ${migration-task-name}
Terminate kbcli migration
-
Check whether there are running migration tasks.
kbcli migration list -
Disable the migration add-on.
kbcli addon disable migration -
Delete the Kubernetes CRD (Custom Resource Definition) manually.
kubectl delete crd migrationtasks.datamigration.apecloud.io migrationtemplates.datamigration.apecloud.io serialjobs.common.apecloud.io