Failure simulation and automatic recovery
As an open-source data management platform, KubeBlocks supports two database forms, ReplicationSet and ConsensusSet. ReplicationSet can be used for single source with multiple replicas, and non-automatic switching database management, such as MySQL and Redis. ConsensusSet can be used for database management with multiple replicas and automatic switching capabilities, such as ApeCloud MySQL RaftGroup with multiple replicas, MongoDB, etc. The ConsensusSet database management capability has been released in KubeBlocks v0.3.0, and ReplicationSet is under development.
This guide takes ApeCloud MySQL as an example to introduce the high availability capability of the database in the form of ConsensusSet. This capability is also applicable to other database engines.
Recovery simulation
The faults here are all simulated by deleting a pod. When there are sufficient resources, the fault can also be simulated by machine downtime or container deletion, and its automatic recovery is the same as described here.
Before you start
-
Install KubeBlocks: You can install KubeBlocks by kbcli or by Helm.
-
Create an ApeCloud MySQL RaftGroup, refer to Create a MySQL cluster.
-
Run
kubectl get cd apecloud-mysql -o yamlto check whether rolechangedprobe is enabled in the ApeCloud MySQL RaftGroup (it is enabled by default). If the following configuration exists, it indicates that it is enabled:probes:
roleProbe:
failureThreshold: 3
periodSeconds: 2
timeoutSeconds: 1
Leader pod fault
Steps:
-
View the ApeCloud MySQL RaftGroup information. View the leader pod name in
Topology. In this example, the leader pod's name is mysql-cluster-1.kbcli cluster describe mysql-cluster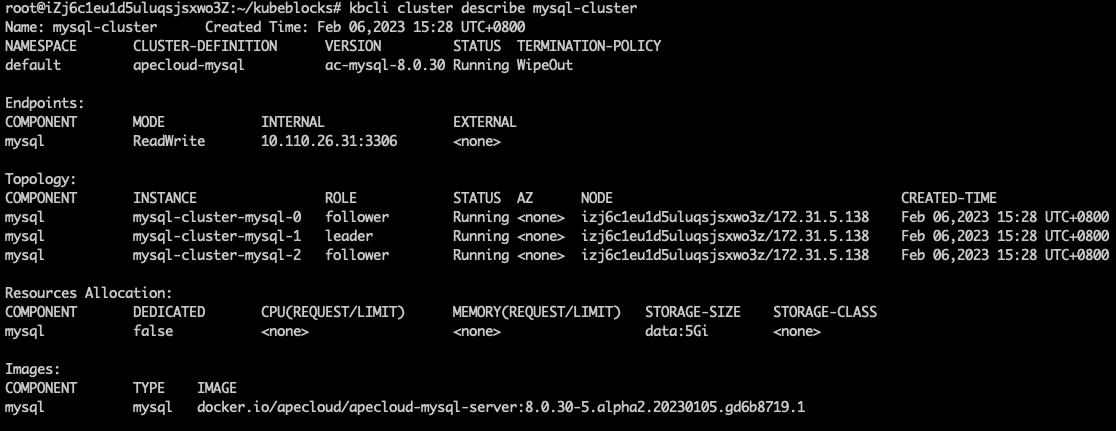
-
Delete the leader pod
mysql-cluster-mysql-1to simulate a pod fault.kubectl delete pod mysql-cluster-mysql-1 -
Run
kbcli cluster describeandkbcli cluster connectto check the status of the pods and RaftGroup connection.Results
The following example shows that the roles of pods have changed after the old leader pod was deleted and
mysql-cluster-mysql-2is elected as the new leader pod.kbcli cluster describe mysql-cluster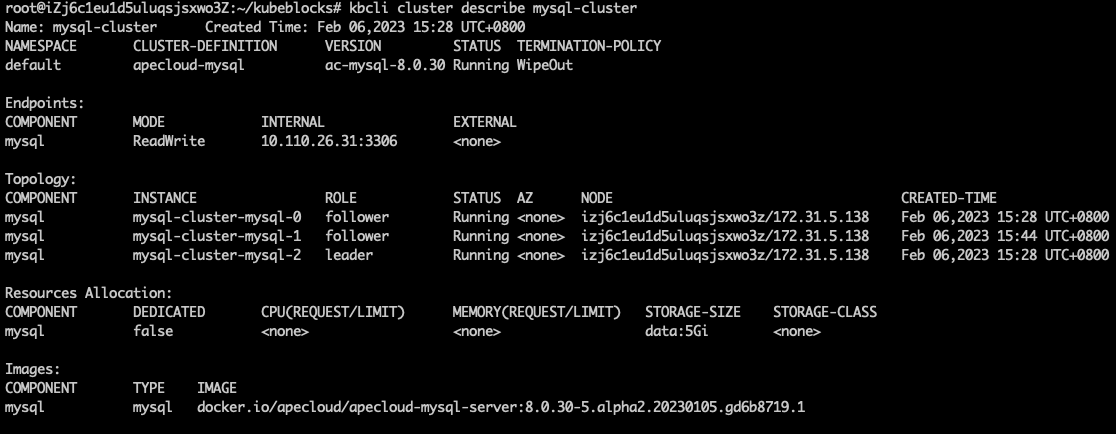 It shows that this ApeCloud MySQL RaftGroup can be connected within seconds.
It shows that this ApeCloud MySQL RaftGroup can be connected within seconds.kbcli cluster connect mysql-cluster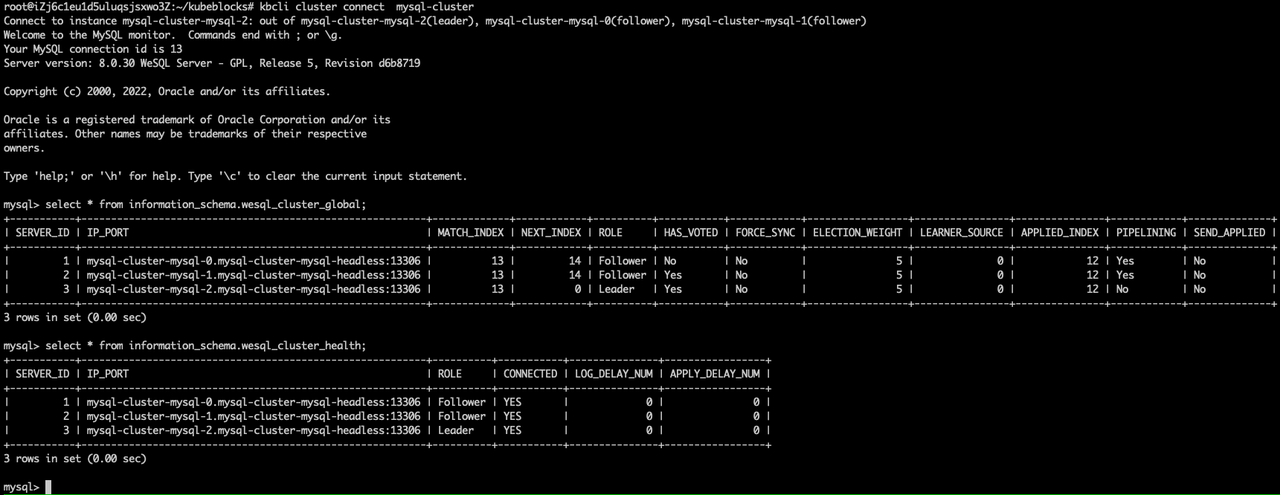
How the automatic recovery works
After the leader pod is deleted, the ApeCloud MySQL RaftGroup elects a new leader. In this example,
mysql-cluster-mysql-2is elected as the new leader. KubeBlocks detects that the leader has changed, and sends a notification to update the access link. The original exception node automatically rebuilds and recovers to the normal RaftGroup state. It normally takes 30 seconds from exception to recovery.
Single follower pod exception
Steps:
-
View the ApeCloud MySQL RaftGroup information and view the follower pod name in
Topology. In this example, the follower pods are mysql-cluster-mysql-0 and mysql-cluster-mysql-2.kbcli cluster describe mysql-cluster
-
Delete the follower pod mysql-cluster-mysql-0.
kubectl delete pod mysql-cluster-mysql-0 -
View the RaftGroup status and you can find the follower pod is being terminated in
Component.Instance.kbcli cluster describe mysql-cluster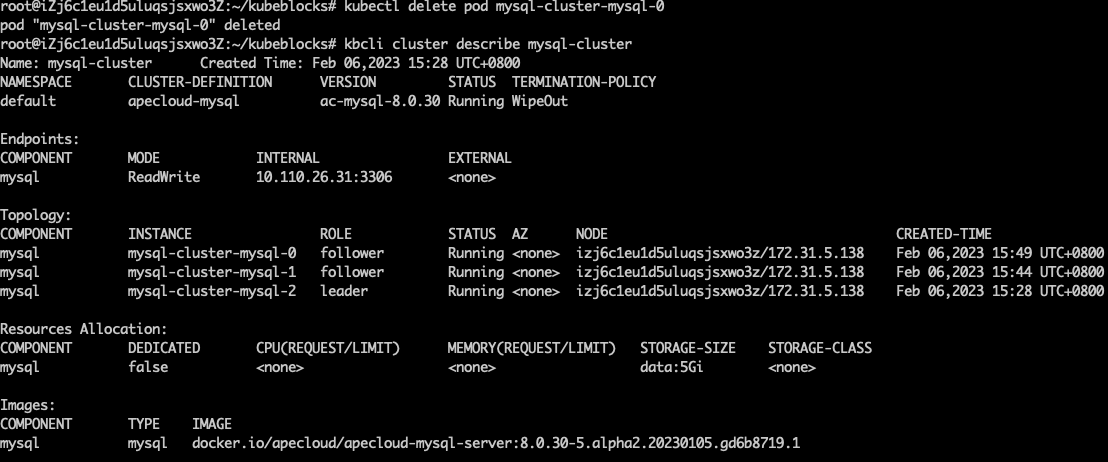
-
Connect to the RaftGroup and you can find this single follower exception doesn't affect the R/W of the cluster.
kbcli cluster connect mysql-cluster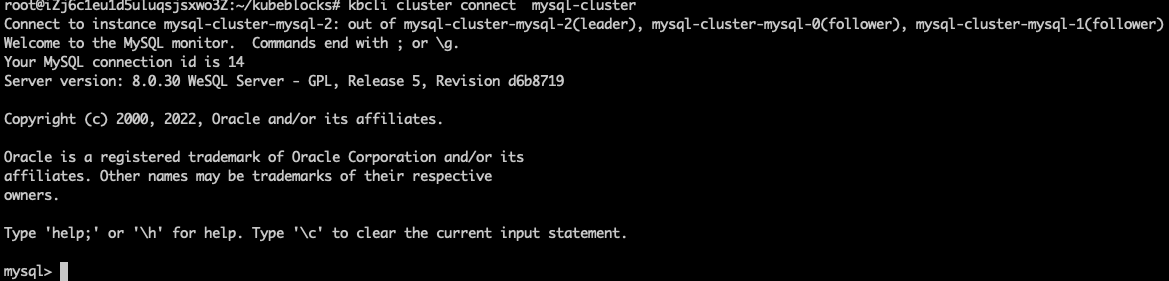
How the automatic recovery works
One follower exception doesn't trigger re-electing of the leader or access link switch, so the R/W of the cluster is not affected. Follower exception triggers recreation and recovery. The process takes no more than 30 seconds.
Two pods exception
The availability of the cluster generally requires the majority of pods to be in a normal state. When most pods are exceptional, the original leader will be automatically downgraded to a follower. Therefore, any two exceptional pods result in only one follower pod remaining.
In this way, whether exceptions occur to one leader and one follower or two followers, failure performance and automatic recovery are the same.
Steps:
-
View the ApeCloud MySQL RaftGroup information and view the follower pod name in
Topology. In this example, the follower pods are mysql-cluster-mysql-1 and mysql-cluster-mysql-0.kbcli cluster describe mysql-cluster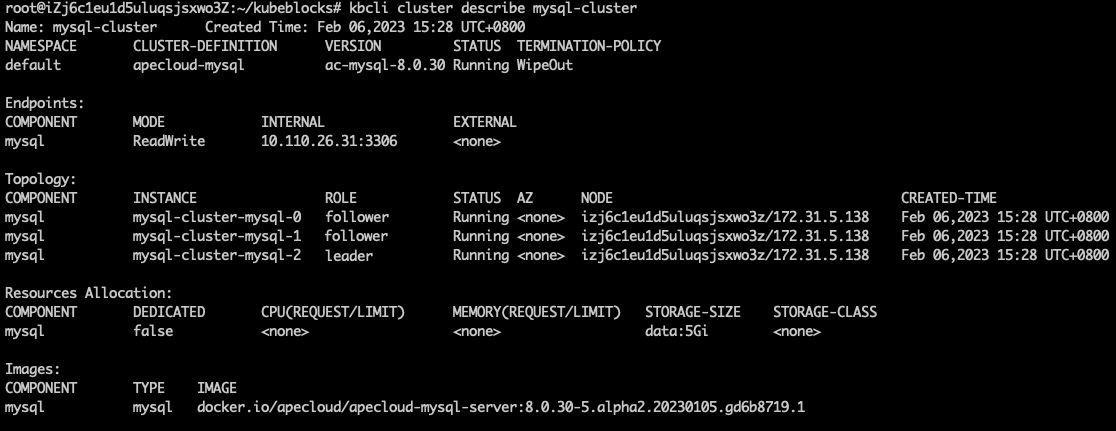
-
Delete these two follower pods.
kubectl delete pod mysql-cluster-mysql-1 mysql-cluster-mysql-0
-
View the RaftGroup status and you can find the follower pods are pending and a new leader pod is selected.
kbcli cluster describe mysql-cluster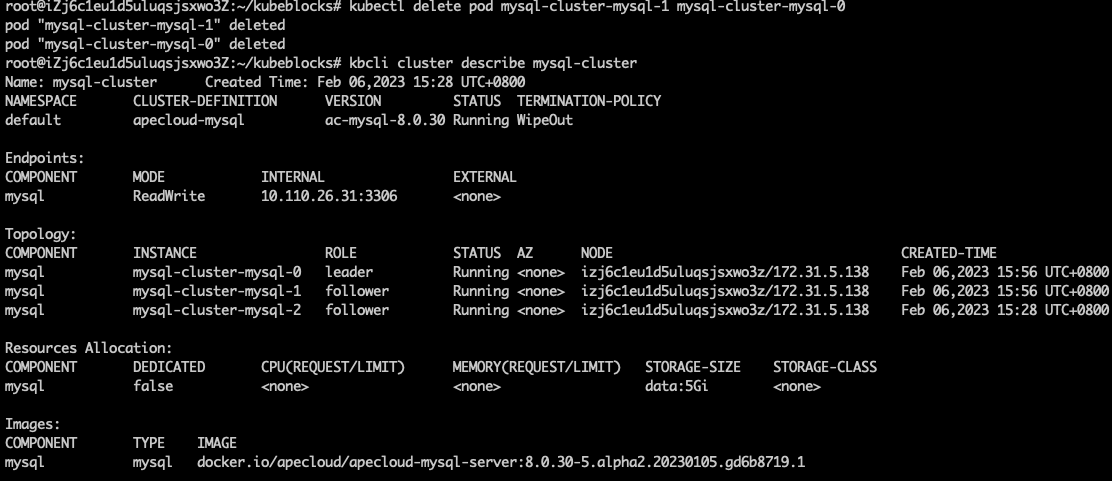
-
Run
kbcli cluster connect mysql-clusteragain after a few seconds and you can find the pods in the RaftGroup work normally again inComponent.Instance.kbcli cluster connect mysql-cluster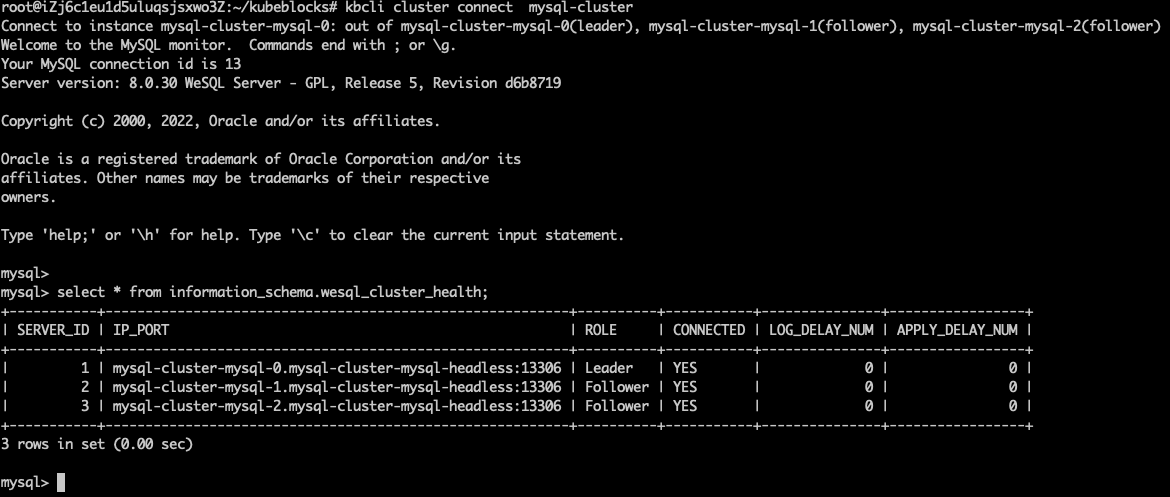
How the automatic recovery works
When two pods of the ApeCloud MySQL RaftGroup are exceptional, pods are unavailable and cluster R/W is unavailable. After the recreation of pods, a new leader is elected to recover to R/W status. The process takes less than 30 seconds.
All pods exception
Steps:
-
Run the command below to view the ApeCloud MySQL RaftGroup information and view the pods' names in
Topology.kbcli cluster describe mysql-cluster
-
Delete all pods.
kubectl delete pod mysql-cluster-mysql-1 mysql-cluster-mysql-0 mysql-cluster-mysql-2
-
Run the command below to view the deleting process. You can find the pods are pending.
kbcli cluster describe mysql-cluster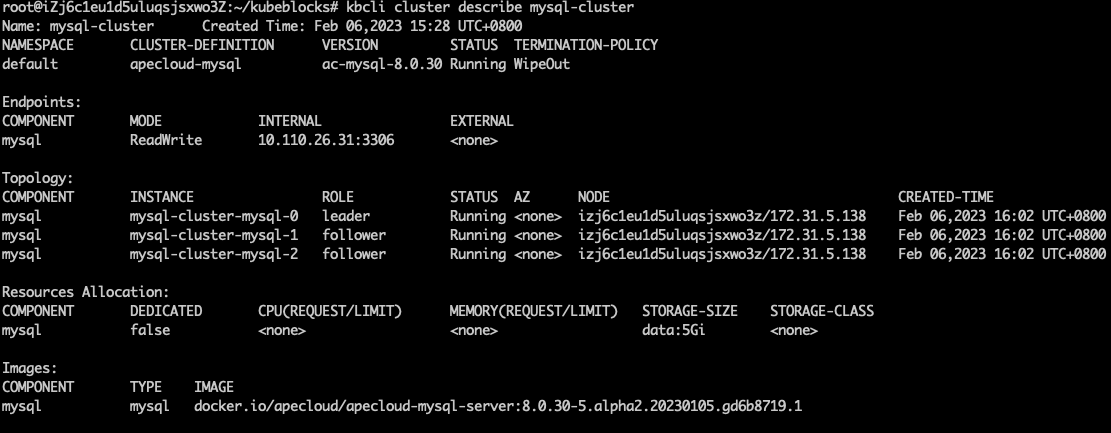
-
Run
kbcli cluster connect mysql-clusteragain after a few seconds and you can find the pods in the RaftGroup work normally again.kbcli cluster connect mysql-cluster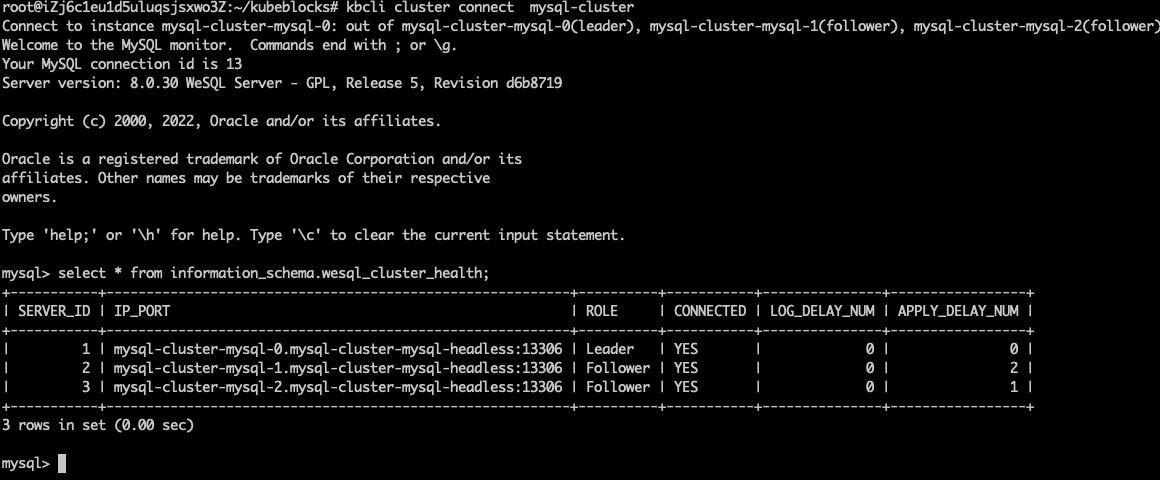
How the automatic recovery works
Every time the pod is deleted, recreation is triggered. And then ApeCloud MySQL automatically completes the cluster recovery and the election of a new leader. After the election of the leader is completed, KubeBlocks detects the new leader and updates the access link. This process takes less than 30 seconds.